So this came up on social media. Someone had been playing with some sample raw footage provided by a camera manufacturer and he/she was concerned because he felt that this manufacturer supplied footage graded much better than his/her own Sony XAVC-I footage.
There is a lot to a situation like this, but very often the issue isn’t that the other footage was raw while his/her own footage was XAVC-I S-Log. Raw doesn’t normally have more colour or more DR than log. The colour range and the shadow range won’t be significantly different as that tends to be limited by the cameras sensor rather than the recording codec. But what you might have if the raw is 12 bit or greater is a larger bit depth or less compression. Perhaps a bit of both and that can sometimes give some extra precision or finer gradations as well as a bit less noise (although compression can reduce noise). This may come into play when you really start to push and pull the footage very hard in the grade, but generally, if you can’t get the image you want out of 10 bit XAVC-I, 12 bit raw isn’t going to help you. Raw might make it a bit quicker to get to where you want to be and I do love working with the 16 bit X-OCN (raw) from Venice and Burano, but I have never really felt that XAVC S-Log3 is lacking. Even a deeper bit depth might not be all it seems. The sensors in most video cameras under $20K only have 12 bit analog to digital converters and that tends to be the main image quality bottleneck (and this where Venice really shines with its 14 bit A2D).
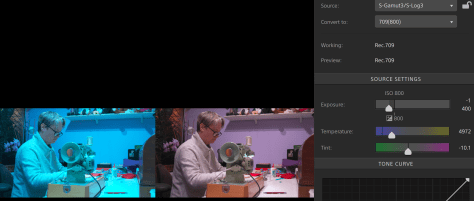
Sony’s XAVC-I S-log3 grades really well, really, really well. A big issue however is the reliance on LUTs. 3D LUTs divide the image up into 33x or 65x adjustment bands and then it is down to the grading software to interpolate between each band. This can introduce artefacts into the image.
Some people simply skip doing a proper colourspace transform altogether and this may introduce twists into the gamma and colourspace which then makes it hard to get the colours or contrast they really want as it can be hard to bend the colours in a pleasing way without them going “weird”.
Colour managed workflows help to maintain the full range of the original content within the correct output colourspace without any unwanted twists and are often the best way to full realise the potential of the content you have shot.
Plus not all grading software is created equal. I was an Adobe Premiere user for years until I needed to do a lot more grading. When DaVinci Resolve became affordable I switched to Resolve for grading and have never looked back – after all it is a proper grading tool, not edit software with a bunch of plugins bolted on.
But as always the real key is how it was shot. Manufacturer supplied sample content is likely to have been shot very well and highly optimised, after all they want it to make their camera look as good as possible. When comparing footage from different sources you really do need to consider whether just how well it was shot. Was the most appropriate exposure index used for the type of scene. Was it shot at the best possible time of day for the best sun positioning. How much attention went in to things like the careful choice of the colours in the scene to provide pleasing colour contrast. How much time was spent with negative fill to bring down the shadow areas etc, what filtration was used to bleed off highlights or polarise the sky or windows. What lenses were used. All these things will have a massive impact on how gradeable the footage will be.
 Over the last few days Sony have been busy releasing new drivers and new software to support not just Venice 2 but also the AXS-R7 and newer AXS-R1 SxS card readers on Apples M1 macs as well as Windows 11.
Over the last few days Sony have been busy releasing new drivers and new software to support not just Venice 2 but also the AXS-R7 and newer AXS-R1 SxS card readers on Apples M1 macs as well as Windows 11.









 Atomos have release a firmware update for the Shogun 7 to correctly implement raw recording from the FX6 at up to 60fps.
Atomos have release a firmware update for the Shogun 7 to correctly implement raw recording from the FX6 at up to 60fps.